Intestinal parasites- These are helminths that parasitize inside the human intestines.It can be either one parasite or several at once.The more helminth is in the body, the more significant health worsens.For a long time, the existing polyiuria leads to a complete depletion of the body.Some migrating representatives can clog the bile ducts and provoke mechanical jaundice.
List of intestinal parasites
In domestic practice, it is somewhat conditionally customary to divide all helminths into tropical and non -ropical.
Tropical parasites are found in countries with the corresponding climate-in Africa, Southeast Asia.These include Schistosomes, Filaria, Wucheria and many others.You can get infected with tropical helminths only in the territory of the corresponding country, tasting local cuisine dishes, using water from an unknown water supply source, neglecting the rules of sanitation and hygiene.
Infection with tropical helminthias of a healthy person from a sick person is impossible, since certain environmental conditions and the body of the intermediate host are necessary to complete the full -fledged development cycle.
Currently, more than 300 parasites are known, about 100 of them are recorded on the European continent.A significant part of them parasitizes precisely in the intestines of a person.
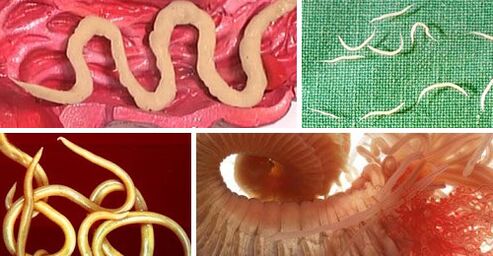
The most common version of the classification of intestinal parasites in accordance with the structure of their body.The following classes are distinguished:
- Supers (they are also called trematodes) - have a leaf -shaped or oval shape, the main distinguishing feature is the presence of suction cups;
- ribbon (they are also called cestodes) - can reach a significant length (up to several meters);have the shape of a lace or flat tape;
- Round (they are also called nematodes) - differ in the corresponding form.
Among the most relevant intestinal human helminthias are known:
| Nematodes | Cestodes | Trematodes |
|
|
|
Each helminth is characterized by the stages of development and the change of several owners.
Symptoms of intestinal parasites
The clinical manifestations of intestinal helminthiasis have much in common, so it is almost impossible to decide on the diagnosis before the laboratory examination.In this regard, one can distinguish an acute and chronic form of helminthiasis and describe the appropriate clinical symptoms.
Acute phase
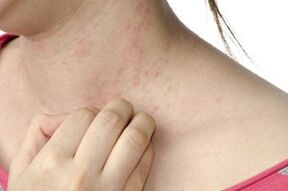
It is characterized by a pronounced general symptoms due to both the action of the parasite itself and the response of the organs and systems of the host.Among the most significant symptoms:
- subfebrile temperature;
- skin rashes of various intensity and species (spots, papules, less often pustules and hemorrhage) often in combination with skin itching;
- pain in the muscles and joints of a spilled nature;
- swelling of the skin and subcutaneous fat;
- Abdominal syndrome (spilled pain in the abdomen, nausea and repeated vomiting, long -term diarrhea without pathological impurities).
The severity of the above clinical features is individual.One person can have a slight malaise, and the other has a sharp deterioration in the state of health, which cannot go unnoticed.
Chronic phase
It occurs in the absence of adequate treatment.Local (intestinal symptoms) associated with mechanical damage to the intestinal wall comes to the fore.General clinical symptoms are less pronounced.As a result of chronic, helminths are found:
- violation of the absorption of nutrients;
- inhibition of metabolism processes (exhaustion, anemia);
- Some helminths provoke the formation of non -lastosis.
A spontaneous cure at the stage of the chronic phase of helminthiasis is almost impossible.
Features of individual types of helminthiases
Only a doctor can assume the development of one or another helminthiasis.Characteristic clinical features are typical only for certain types of helminths.For example:
| pinworm |
|
| Askarida |
|
| trichinosis |
|
| Anquilostomidosis |
|
| Trichocephalosis | damage to the distal intestines (hemocolite); |
| Strongyloidosis | Atrophy of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines; |
| echinococcus | mechanical jaundice as a result of the formation of an echinococcal cyst in the gates of the liver; |
| Cat bicom | potentiation of carcinogenesis |
Confirmation of the diagnosis of one or another helminthosis is possible only after a comprehensive examination.
How is the infection and development of the parasite in the body

Infection with intestinal parasites can occur in 2 ways:
- through the skin - the so -called percutated path;
- Through dirty hands, poorly washed vegetables and fruits, contaminated water and food.
The intestinal parasites, in accordance with their name, do not leave the limits of the digestive canal of a person.In the future, the parasite can develop in 2 ways: simple and complex.
With a simple cycle of development from an egg, a helminth that enters the human body, its adult individual develops.Clinical symptoms are due to damage to a particular gastrointestinal department.
With a complex development cycle, a larva forms from the egg, and the parasite is migrated to several organs, which determines the variety of clinical symptoms.
Methods for diagnosing parasitic intestinal diseases
For the diagnosis and treatment of parasitic diseases of the intestine, you should consult a doctor-infectious disease specialist.In large cities there are special medical centers and even stationary departments.
Diagnosis of helminthic invasion begins with a general clinical blood test: the main distinguishing feature is pronounced eosinophilia - an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood.
Among the specific research methods are known:
- The parasitological method is the detection of worms in feces in the patient;For this, a fresh portion of feces is collected and examined under a microscope;If necessary, a transport environment is used to deliver to the laboratory;
- The serological method is the detection of class m immunoglobulins (acute phase);
- Instrumental methods (ultrasound, tomography) - with the aim of differential diagnosis to exclude tumor processes.
The result of only one study is not an independent diagnosis.Only a doctor can assess the patient's condition, only a doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis.
Treatment
Therapy of any helminthiasis should be under the control of the doctor.The independent use of antigelmic drugs (including for prevention) is unacceptable, since most drugs are quite toxic.
A comprehensive approach is required, including dietary nutrition, medicines and folk remedies.
Nutrition
There are no strict rules regulating nutrition for helminthiasis.It is enough to follow the rules of healthy diet:
- use a sufficient amount of low -fat dairy products;
- include a variety of porridge, egg dishes, low -fat varieties of fish and meat in the diet;
- abandon alcoholic beverages;
- reduce or exclude semi -finished products, soda water, products with a high content of preservatives and flavor enhancers;
- All products should be thoroughly washed (vegetables, fruits, berries), if possible - thermally processed (the Bifsteke with blood is not allowed) in order to prevent re -infection.
When prescribing a particular drug, the doctor individually will explain which products should be limited or completely excluded.
Drugs
In the treatment of helminthias, universal drugs are used that destroy several types of helminths at once.
The duration of the course of treatment is selected individually.In combination with antiparasitic drugs, hepatoprotectors and enterosorbents are used.
Cleansing of worms
The use of some anthelmintic agents involves its combination with an enema.The enema - an ordinary cleansing enema - there are no features.Whether it is needed or not, the doctor decides.
Folk recipes

The effectiveness is doubtful.Among those who are popular, they are known:
- pumpkin seeds;
- alcohol tincture made of non -elated (green) walnuts;
- alcohol tincture of chanterelles;
- Freshly prepared broth made of pine cones.
A combination of folk prescriptions and traditional drugs is quite allowed.
Prevention of parasitic diseases
There are no specific prevention.Given the simplicity and ease of infection, it is very difficult to protect yourself from helminthic invasion.This is necessary:
- always wash vegetables and fruits, rinse them with boiling water;
- prevent storage in the refrigerator with a number of products of finished and semi -finished products;
- mandatory and thoroughly wash your hands;
- Follow the rules of culinary processing of dishes.




